Abstract
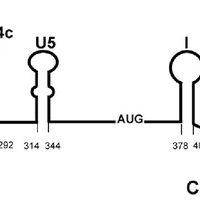
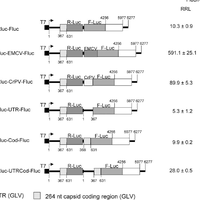
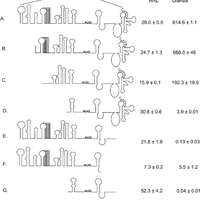
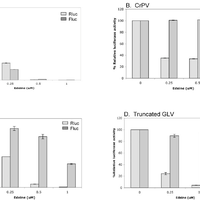
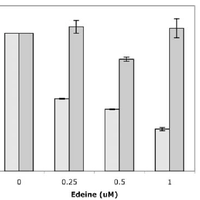
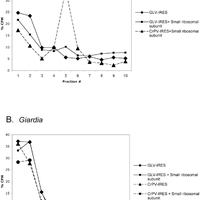
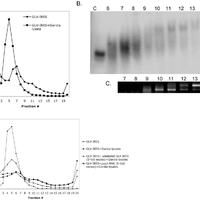
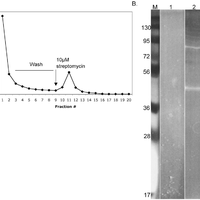
Giardiavirus (GLV) utilizes an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) for translation initiation in the early branching eukaryote Giardia lamblia. Unlike most of the viral IRESs among higher eukaryotes, which localize primarily within the 5′-untranslated region (UTR), the GLV IRES comprises 253 nts of 5′UTR and the initial 264 nts in the open-reading-frame (ORF). To test if GLV IRES also functions in higher eukaryotic systems, we examined it in rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL) and found that it functions much less efficiently than the IRES from the Encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) or Cricket paralysis virus (CrPV). In contrast, both EMCV-IRES and CrPV-IRESs were inactive in transfected Giardia cells. Structure-function analysis indicated that only the stem-loop U5 from the 5′UTR and the stem-loop I plus the downstream box (Dbox) from the ORF of GLV IRES are required for limited IRES function in RRL. Edeine, a translation initiation inhibitor, did not significantly affect the function of GLV IRES in either RRL or Giardia, indicating that a pre-initiation complex is not required for GLV IRES - mediated translation initiation. However, the small ribosomal subunit purified from Giardia did not bind to GLV IRES, indicating that additional protein factors may be necessary. A member of the helicase family IBP1 and two known viral IRES binding proteins La autoantigen and SRp20 have been identified in Giardia that bind to GLV IRES in vitro. These three proteins could be involved in facilitating small ribosome recruitment for initiating translation. © 2009 Garlapati, Wang.
Figures
Register to see more suggestions
Mendeley helps you to discover research relevant for your work.
Cite
CITATION STYLE
Garlapati, S., & Wang, C. C. (2009). Giardiavirus internal ribosome entry site has an apparently unique mechanism of initiating translation. PLoS ONE, 4(10). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0007435