Abstract
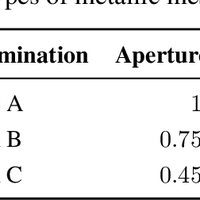
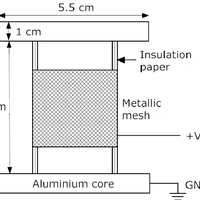
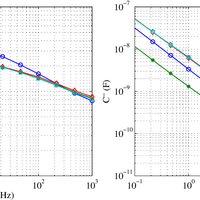
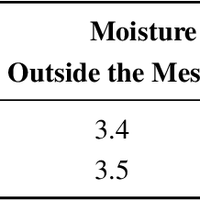
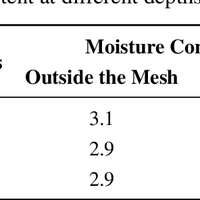
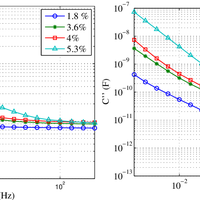
Moisture is an important variable that must be kept under control to guarantee a safe operation of power transformers. Because of the hydrophilic character of cellulose, water mainly remains in the solid insulation, while just a few parts per million are dissolved in oil. The distribution of moisture between paper and oil is not static, but varies depending on the insulation temperature, and thus, water migration processes take place continuously during transformers operation. In this work, a sensor is presented that allows the determination of the moisture content of the transformer solid insulation in the steady state and during the moisture migration processes. The main objective of the design is that the electrodes of the sensor should not obstruct the movement of water from the solid insulation to the oil, so the proposed prototype uses a metallic-mesh electrode to do the measurements. The measurement setup is based on the characterization of the insulation dielectric response by means of the frequency dielectric spectroscopy (FDS) method. The sensitivity of the proposed sensor has been tested on samples with a moisture content within 1% to 5%, demonstrating the good sensitivity and repeatability of the measurements.
Figures
Author supplied keywords
Register to see more suggestions
Mendeley helps you to discover research relevant for your work.
Cite
CITATION STYLE
García, B., García, D., & Robles, G. (2015). Development of a Moisture-In-Solid-Insulation sensor for power transformers. Sensors (Switzerland), 15(2), 3610–3624. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150203610