Abstract
We report on scaling and timing tests of the SIESTA electronic structure code for ab initio molecular dynamics simulations using density-functional theory. The tests are performed on six large-scale supercomputers belonging to the PRACE Tier-0 network with four different architectures: Cray XE6, IBM BlueGene/Q, BullX, and IBM iDataPlex. We employ a systematic strategy for simultaneously testing weak and strong scaling, and propose a measure which is independent of the range of number of cores on which the tests are performed to quantify strong scaling efficiency as a function of simulation size. We find an increase in efficiency with simulation size for all machines, with a qualitatively different curve depending on the supercomputer topology, and discuss the connection of this functional form with weak scaling behaviour. We also analyze the absolute timings obtained in our tests, showing the range of system sizes and cores favourable for different machines. Our results can be employed as a guide both for running SIESTA on parallel architectures, and for executing similar scaling tests of other electronic structure codes. © 2014 Fabiano Corsetti.
Figures
Register to see more suggestions
Mendeley helps you to discover research relevant for your work.
Cite
CITATION STYLE
Corsetti, F. (2014). Performance analysis of electronic structure codes on HPC systems: A case study of SIESTA. PLoS ONE, 9(4). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095390

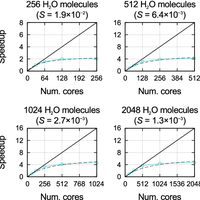
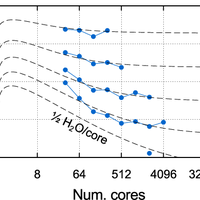
![Figure 3. Strong scaling and efficiency. Top panel: S value as a function of system size fitted to strong scaling data obtained with SIESTA on the six machines; also included are values calculated with other DFT codes for a single system size on IBM BlueGene architectures (ABINIT: 108 atoms, 1188 electrons, 3D system, 4 k points [42]; VASP: 87 atoms, 822 electrons, 2D system, 14 k points [42]; CPMD: 284 atoms, 1192 electrons, 3D system, k-point sampling unspecified [42]; QE: 1532 atoms, 5232 electrons, 1D system, C point [27,42]; Qbox: 1000 atoms, 12000 electrons, 3D system, C point [11]). Bottom panel: relationship between S and core hour efficiency as a function of the number of cores, for four different values of S given by the black dashed lines, and the fitted values of S obtained with SIESTA on four different machines for a system of 4096 water molecules; the number of cores at which the efficiency is equal to 50% is labelled in each case. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0095390.g003](https://s3-eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/com.mendeley.prod.article-extracted-content/images/871a38eb-b38d-365d-84b4-66d0ae23f952/thumbnail-470b3f0c-559c-49ff-b661-d28e2aa83498-2.png)